AI
-
In the previous article, we dived deep into the lives and inventions of many computer pioneers and the challanges the faced. In this article we are going to explore the…
-
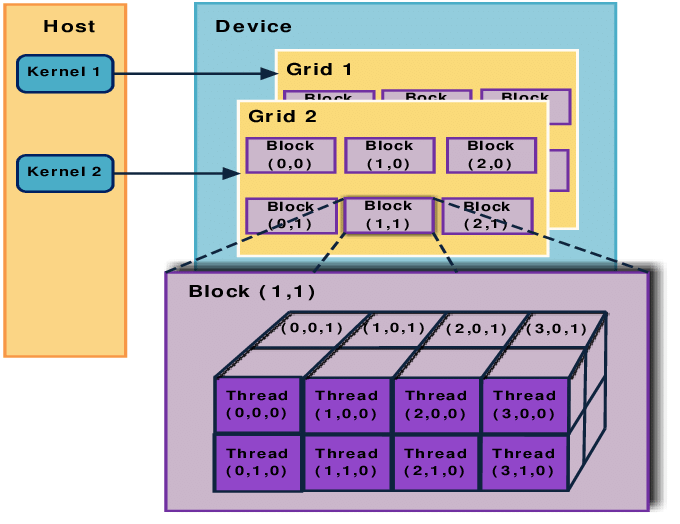
CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a parallel computing platform and programming model developed by NVIDIA. It enables developers to harness the power of NVIDIA GPUs for general-purpose processing tasks,…
-
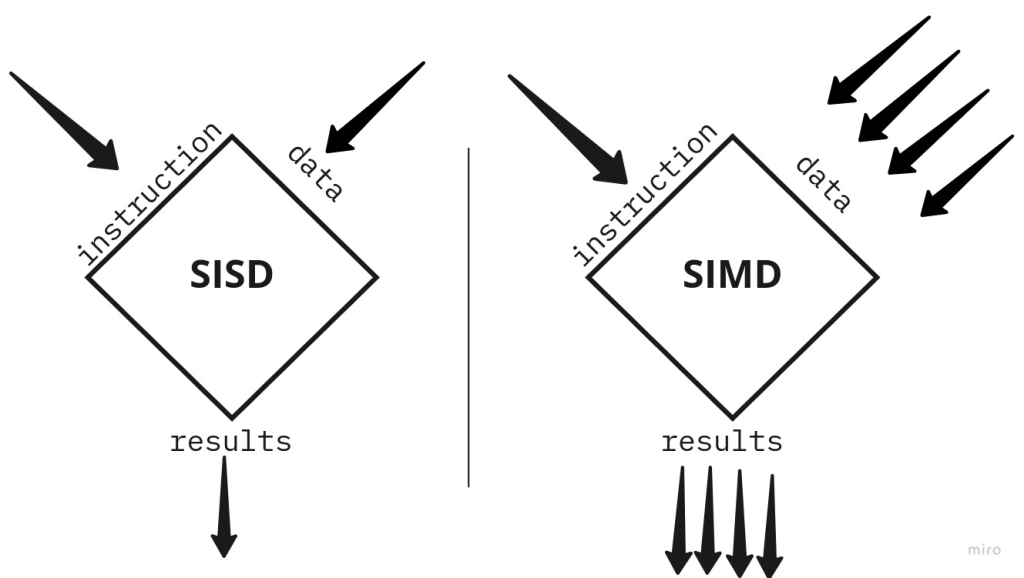
SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) is a parallel computing model that allows a single operation (instruction) to be applied to multiple data points simultaneously. The primary reasons for using SIMD…
-
A software-defined vehicle (SDV) prioritizes software over hardware in its operation, unlike traditional vehicles that are built around a mechanical framework. SDVs use software to enable vehicle functionality, which is…
-
Apollo 13 intended as the third lunar landing had just lost two fuel cells and was venting oxygen into space 200,000 miles from Earth, soon the second oxygen tank would…
-
AMD ROCm™ is an open software stack including drivers, development tools, and APIs that enable GPU programming from low-level kernel to end-user applications. ROCm is optimized for Generative AI and…
-
In this extremely dynamic landscape of machine learning, somebody tried to reinvent ML itself giving us KANs: Kolmogorov Arnold Network. This approach challenges the conventional way of using Multi-Layer Perceptron(MLPs). …
-
Discover how Arduino and TensorFlow Lite Micro bring powerful machine learning capabilities to the tiny Nano 33 BLE Sense, enabling innovative, sensor-driven applications without extra hardware. Dive into the future…
-
llama.cpp is a project that aims to provide a lightweight, efficient, and portable implementation of Meta’s LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI) models. This implementation is particularly designed to enable…
-
The use of specialized processors such as GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), NPUs (Neural Processing Units), or DSPs (Digital Signal Processors) for hardware acceleration can significantly enhance the performance of inference…